You are here
Report #5 - Controlling VRep Robot with Clarion
0. PROJECT DELIVERABLES
This section is available in this report for making easy the access to the source code and executables. Notice that, due to the nature of the language framework used in this implementation, it requires either a Windows OS with .NET Framework 4.0 or a system with Mono and a compatible .NET Framework 4.0 available.
The project source code is available for downlading here.
The executable files can be found for downlading here.
The VREP Scene is also available for downlading here.
For running the project perform the following steps:
- Open VREP scene that is available for downloading above and start the simulation using VREP menu Simulation > Start simulation.
- Once the simulation is running, start the ClarionDEMO application by either using the available source ou running the compiled executable.
Notice that on Linux or OSX machines it requires Mono to be available.
1. INTRODUCTION
The Virtual Robot Experimentation Platform (VREP) is a simulation environment used for prototyping that helps creating embedded applications for robots without the need of the actual hardware. It contains an extensive library with many types of robots, sensors and objects for supporting creating the simulation scene. It provides APIs for interacting with the available robots and sensors that can be accessed remotely or locally. The picture following shows a screenshop of VREP smiulation environment. VREP is available for download here. More information about the available VREP features can be found here.
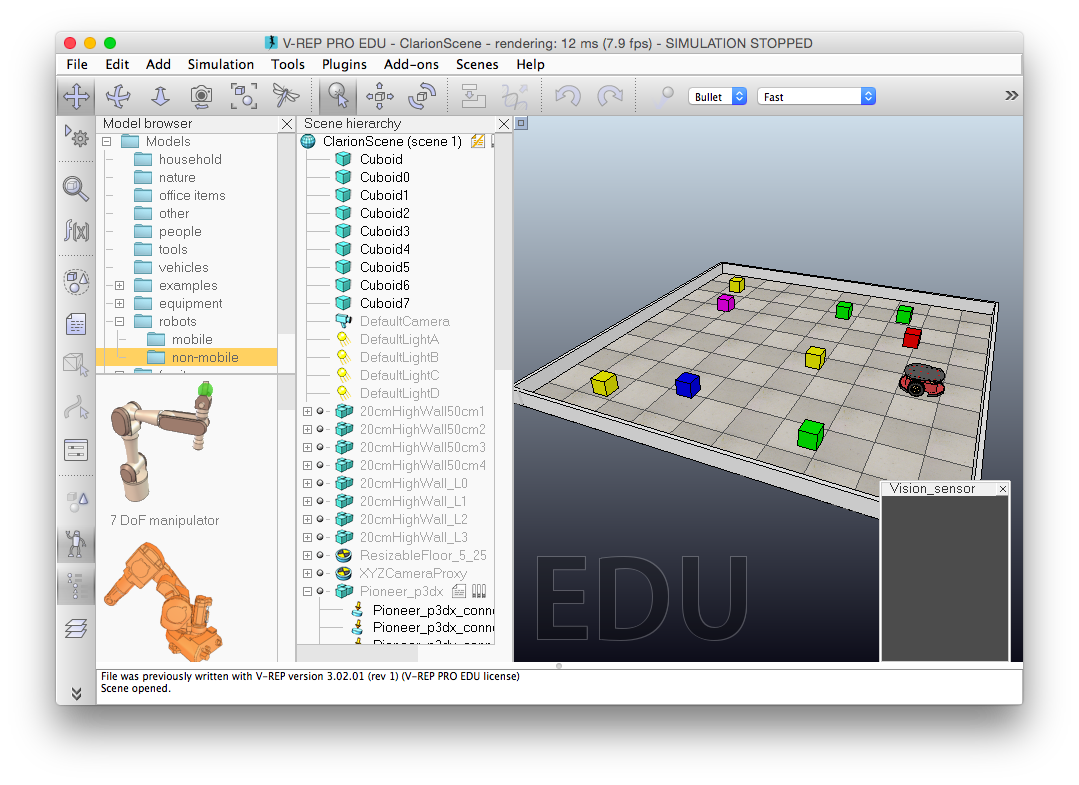
Figure 1 - The VREP simulation environment.
The Connectionist Learning with Adaptive Rule Induction On-line (Clarion) is a cognitive framework that simulate several cognitive tasks supporting the implementation of artificial intelligent applications. More information about Clarion framework can be found here.
The objective of this project is to connect a Clarion cognitive application to a VREP robot, using the available VREP remote API, so that the Robot can perform actions received from the cognitive application based on the robot's perceptions of the surrounding environment.
2. THE SOLUTION OVERVIEW
VREP has APIs for remote connection with libraries available for languages like Java and C++ but does not provide libraries for C#. Clarion framework, on the other hand, is developed in C# and for this project a different solution for remote connection had to be used.
When creating a scene in VREP, the environment allows the use of some LUA scripts, attached to the scene's objects, that run when the scene simulation is executed. For this project, it was developed a script that was attached to the robot for starting a UDP server and later listening to received requests.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
-- Initialization code area if (sim_call_type==sim_childscriptcall_initialization) then ... -------------------------------------------------- -- UDP -------------------------------------------------- local socket = require("socket") server = assert(socket.udp()) assert(server:setsockname(address,port)) server:settimeout(0) send = function(...) server:sendto(..., clientIp, clientPort) end sendln = function(...) server:sendto(... .. "\n", clientIp, clientPort) end -------------------------------------------------- ... end |
Code Snippet 1 - UDP server implemented in VREP script.
The script has an initialization region, called sim_childscriptcall_initialization, that runs only once then the script is started, and it is in that region that the UDP server code is implemented.
Once the connection is started, all the received commands are received inside the sim_childscriptcall_actuation code region that is executed all the time during the simulation in a sort of loop. As show by the code snippet that follows, the remote commands are received by the command server:receiveFrom().
1 2 3 4 5 |
if (sim_call_type==sim_childscriptcall_actuation) then ... command, clientIp, clientPort = server:receivefrom() ... end |
Code Snippet 2 - UDP server receive data implementation.
Together with the remote connectivity code, many other lines of code are implemented in VREP Scene script for receiving remote commands and translating them to moviments and sensor readings during the simulation. The complete script code is available for donwload here.
A very basic picture of the connectivity architecture of Clarion application and VREP environment is shown in the picture following. Apart from the LUA scripts in VREP Scene, there is also a library in C# developed for enabling the connectivity between the framework and the simulation environment. The C# library contains high-level abstractions that represent objects, sensors and actions in the Scence.

Figure 2 - Clarion-VREP proxy architecture.
The main piece of code in C# for sending and receiving commands to VREP Scene is shown in the following code snippet.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 |
using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Net; using System.Net.Sockets; using System.Text; using VRepProxy.Objects; namespace VRepProxy.Proxy { public class VRepProxy { private static UdpClient udpClient; private static IPEndPoint endPoint; private static String host; private static int port; private const int socketReadDelay = 30; private Scene scene; public VRepProxy(String host, int port){ VRepProxy.host = host; VRepProxy.port = port; Connect (); } public static void Connect() { if (udpClient == null || endPoint == null) { udpClient = new UdpClient (); udpClient.Client.ReceiveBufferSize = 1024; endPoint = new IPEndPoint (IPAddress.Parse (host), port); } udpClient.Connect (endPoint); } public static void ReleaseConnection() { if (udpClient == null || endPoint == null) { udpClient.Close (); } } public Scene GetScene(){ if (scene == null) { scene = new Scene (); } return scene; } public static Boolean Perform(String command){ byte[] sendByte = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes (command); udpClient.Send (sendByte, sendByte.Length); return true; } public static String Get(String command){ String sensors = null; byte[] sendByte = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes (command); udpClient.Send (sendByte, sendByte.Length); while (true) { try { var receivedData = udpClient.Receive (ref endPoint); String data = Encoding.ASCII.GetString (receivedData); sensors = data.Substring (0, data.IndexOf (Environment.NewLine)); break; } catch (System.Net.Sockets.SocketException ex) { if (ex.ErrorCode != 10060) { break; } } System.Threading.Thread.Sleep (socketReadDelay); } return sensors; } } } |
Code Snippet 3 - VRepProxy librayr VRepProxy.cs implementation.
The main piece of code in C# for sending and receiving commands to VREP Scene is shown in the following code snippet. The other proxy objects are shown in the picture following. As shown in the picture, the proxy library is called VRepProxy. All the additional objects can also be seen in the picture that follows. As mentioned before, each object in the Objects package represents an object or a set of objects in VRep Scene.
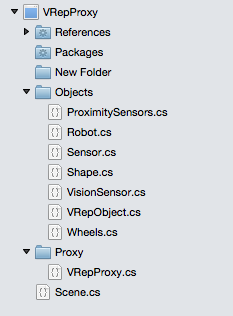
Figure 3 - VRepProxy project structure.
The Clarion agent responsible for receiving the perceptions from sensorial inputs and provide output actions based on cognitive decisions is implemented in VRepAgent library project. The library is composed of a single class, which the code is available following.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 |
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Clarion; using Clarion.Framework; using Clarion.Framework.Core; using Clarion.Framework.Templates; using VRepProxy.Objects; using System.Threading; namespace ClarionSimulation { public delegate Perceptions InputVisualSensorialInformationEventHandler(); public delegate void OutputActionChunkEventHandler(ClarionAgentActionType externalAction); public enum ClarionAgentActionType { DO_NOTHING, ROTATE, MOVE, LEFT, RIGHT, BACK, } public class ClarionAgent { #region Constants private String DIMENSION_SENSOR = "SensorialInformation"; private String DIMENSION_TARGET_AHEAD = "TargetAhead"; private String DIMENSION_SOMETHING_AT_FRONT = "SomethingAtFront"; private String DIMENSION_SOMETHING_AT_LEFT = "SomethingAtLeft"; private String DIMENSION_SOMETHING_AT_RIGHT = "SomethingAtRight"; private String DIMENSION_SOMETHING_AT_BACK = "SomethingAtBack"; #endregion #region Properties #region Simulation public double MaxNumberOfCognitiveCycles = -1; private double CurrentCognitiveCycle = 0; public Int32 TimeBetweenCognitiveCycles = 5; private Thread runThread; #endregion #region Agent private Clarion.Framework.Agent CurrentAgent; /// For each cognitive cycle, this event will /// be called in order to the agent /// receives the current sensorial information public event InputVisualSensorialInformationEventHandler OnNewVisualSensorialInformation; /// For each cognitive cycle, this event will /// be called when the agent selects one action public event OutputActionChunkEventHandler OnNewExternalActionSelected; #endregion #region Perception Input private DimensionValuePair InputTargetAhead; private DimensionValuePair InputSomethingAtFront; #endregion #region Action Output private ExternalActionChunk OutputMove; private ExternalActionChunk OutputLeft; private ExternalActionChunk OutputRight; private ExternalActionChunk OutputBack; #endregion #endregion #region Constructor public ClarionAgent() { // Initialize the agent CurrentAgent = World.NewAgent("Current Agent"); // Initialize Input Information InputTargetAhead = World.NewDimensionValuePair(DIMENSION_SENSOR, DIMENSION_TARGET_AHEAD); InputSomethingAtFront = World.NewDimensionValuePair(DIMENSION_SENSOR, DIMENSION_SOMETHING_AT_FRONT); // Initialize Output actions OutputMove = World.NewExternalActionChunk(ClarionAgentActionType.MOVE.ToString()); OutputLeft = World.NewExternalActionChunk(ClarionAgentActionType.LEFT.ToString()); OutputRight = World.NewExternalActionChunk(ClarionAgentActionType.RIGHT.ToString()); OutputBack = World.NewExternalActionChunk(ClarionAgentActionType.BACK.ToString()); //Create thread to simulation runThread = new Thread(RunThread); Console.WriteLine("Agent started"); } #endregion #region Public Methods public void Run() { Console.WriteLine ("Running Simulation ..."); // Setup Agent to run if (runThread != null && !runThread.IsAlive) { SetupAgentInfraStructure(); if (OnNewVisualSensorialInformation != null) { // Start Simulation Thread runThread.Start(null); } } } public void Abort(Boolean deleteAgent) { Console.WriteLine ("Aborting ..."); if (runThread != null && runThread.IsAlive) { runThread.Abort(); } if (CurrentAgent != null && deleteAgent) { CurrentAgent.Die(); } } #endregion #region Setup Agent Methods private void SetupAgentInfraStructure() { // Setup the ACS Subsystem SetupACS(); } private void SetupMS() { //RichDrive } private void SetupACS() { SupportCalculator moveSupportCalculator = FixedRuleDelegateMove; FixedRule ruleMove = AgentInitializer.InitializeActionRule(CurrentAgent, FixedRule.Factory, OutputMove, moveSupportCalculator); CurrentAgent.Commit(ruleMove); SupportCalculator avoidCollisionFrontSupportCalculator = FixedRuleDelegateAvoidColissionAtFront; FixedRule ruleAvoidCollisionFront = AgentInitializer.InitializeActionRule(CurrentAgent, FixedRule.Factory, OutputBack, avoidCollisionFrontSupportCalculator); CurrentAgent.Commit(ruleAvoidCollisionFront); // Disable Rule Refinement CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.PERFORM_RER_REFINEMENT = false; // The selectio type will be probabilistic CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.LEVEL_SELECTION_METHOD = ActionCenteredSubsystem.LevelSelectionMethods.STOCHASTIC; // The selection of the action will be fixed (not variable) i.e. only the statement defined above. CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.LEVEL_SELECTION_OPTION = ActionCenteredSubsystem.LevelSelectionOptions.FIXED; // Define Probabilistic values CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.FIXED_FR_LEVEL_SELECTION_MEASURE = 1; CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.FIXED_IRL_LEVEL_SELECTION_MEASURE = 0; CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.FIXED_BL_LEVEL_SELECTION_MEASURE = 0; CurrentAgent.ACS.Parameters.FIXED_RER_LEVEL_SELECTION_MEASURE = 0; } //Robot robot; /// <summary> /// Make the agent perception. In other words, translate the information that came /// from sensors to a new type that the agent can understand /// </summary> /// <param name="sensorialInformation">The information that came from server</param> /// <returns>The perceived information</returns> private SensoryInformation MakePerceptionFromSensorialInput(Perceptions sensorialInformation) { SensoryInformation si = World.NewSensoryInformation(CurrentAgent); double[] d = sensorialInformation.getPerceivedDistance (); //Coligion at Front // 00, 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 // 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 //Coligion at Left // 00, 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 // 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 //Coligion at Right // 00, 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 // 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1 //Go to Target Double minFront = (new Double [6] {d[1], d[2], d[3], d[4], d[5], d[6]}).Min (); String color = sensorialInformation.getPerceivedColor (); Boolean target = ((color == Shape.SHAPE_BLUE) || (color == Shape.SHAPE_RED) || (color == Shape.SHAPE_PINK)) && (minFront > 0.2); double targetAheadActivationValue = target ? CurrentAgent.Parameters.MAX_ACTIVATION : CurrentAgent.Parameters.MIN_ACTIVATION; si.Add(InputTargetAhead, targetAheadActivationValue); Boolean somethingAtFront = minFront < 0.2 ; double somethingAtFrontActivationValue = somethingAtFront ? CurrentAgent.Parameters.MAX_ACTIVATION : CurrentAgent.Parameters.MIN_ACTIVATION; si.Add (InputSomethingAtFront, somethingAtFrontActivationValue);
return si;
}
#endregion
#region Delegate Methods
#region Fixed Rules
private double FixedRuleDelegateAvoidColissionAtFront(ActivationCollection currentInput, Rule target)
{
return ((currentInput.Contains(InputSomethingAtFront, CurrentAgent.Parameters.MAX_ACTIVATION))) ? 1.0 : 0.0;
}
private double FixedRuleDelegateMove(ActivationCollection currentInput, Rule target)
{
return ((currentInput.Contains(InputTargetAhead, CurrentAgent.Parameters.MAX_ACTIVATION))) ? 1.0 : 0.0;
}
#endregion
#region Run Thread Method
private void RunThread(object obj)
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting Cognitive Cycle ... press CTRL-C to finish !");
// Cognitive Cycle starts here getting sensorial information
while (CurrentCognitiveCycle != MaxNumberOfCognitiveCycles)
{
// Get current sensorial information
Perceptions sensorialInformation = OnNewVisualSensorialInformation();
// Make the perception
SensoryInformation si = MakePerceptionFromSensorialInput(sensorialInformation);
//Perceive the sensory information
CurrentAgent.Perceive(si);
//Choose an action
ExternalActionChunk chosen = CurrentAgent.GetChosenExternalAction(si);
// Get the selected action
String actionLabel = chosen.LabelAsIComparable.ToString();
ClarionAgentActionType actionType
= (ClarionAgentActionType)Enum.Parse(typeof(ClarionAgentActionType), actionLabel, true);
// Call the output event handler if (OnNewExternalActionSelected != null) { OnNewExternalActionSelected(actionType); } // Increment the number of cognitive cycles CurrentCognitiveCycle++; //Wait to the agent accomplish his job if (TimeBetweenCognitiveCycles > 0) { Thread.Sleep(TimeBetweenCognitiveCycles); } } } #endregion #endregion } } |
Code Snippet 4 - VRepAgent library ClarionAgent.cs implementation.
ClarionDEMO is the main project that makes use of both VRepProxy and VRepAgent libraries. It perform the Robot sensor reading and translate them into actions according to the decisions made by the cognitive system. The main class of the project is called Main.cs and its code is shown in the code snippet that follows.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 |
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Globalization; using System.Linq; using System.Threading; using ClarionSimulation; using VRepProxy; using VRepProxy.Objects; using System.Text.RegularExpressions; namespace ClarionDEMO { class MainClass { #region properties private ClarionAgent agent; private static Scene scene; private Robot robot; private static int nextSide = 0; private static int ucounter = 0; private static int currentSide = 0; #endregion #region constructor //Dictionary<string, LeafletItem> Consolidatedleaflets; //Dictionary<string,int> leafletsTotal = new Dictionary<string,int>(); //Dictionary<string,int> leafletsCollected = new Dictionary<string,int>(); public MainClass () { Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 7 ? 1 : 2) : 0; Console.WriteLine ("Clarion-VRep Demo V0.4"); agent = new ClarionAgent (); agent.OnNewVisualSensorialInformation += new InputVisualSensorialInformationEventHandler (agent_OnNewVisualSensorialInformationHandler); agent.OnNewExternalActionSelected += new OutputActionChunkEventHandler (agent_OnNewExternalActionSelectedHandler); scene = new Scene(); robot = scene.GetRobot (); agent.Run (); } #endregion #region Methods public static void Main (string[] args) { new MainClass (); } Perceptions agent_OnNewVisualSensorialInformationHandler () { //Console.Out.WriteLine ("Sensorial Info Handler"); Perceptions perceptions = null; if (scene != null) { perceptions = robot.GetPerceptions (); switch (perceptions.getPerceivedColor ()) { case Shape.SHAPE_BLIND: Console.Out.WriteLine ("I am blind. "); Console.Out.WriteLine ("Cannot connect to the body."); Environment.Exit (-1); break; case Shape.SHAPE_NOTHING: Console.Out.WriteLine ("I see " + perceptions.getPerceivedColor ()); break; case Shape.SHAPE_GRAY: break; case Shape.SHAPE_BLUE: case Shape.SHAPE_PINK: case Shape.SHAPE_RED: Console.Out.WriteLine ("I see " + perceptions.getPerceivedColor () + " color" + " (--> target)"); break; case Shape.SHAPE_GREEN: case Shape.SHAPE_WHITE: case Shape.SHAPE_YELLOW: Console.Out.WriteLine ("I see " + perceptions.getPerceivedColor () + " color"); break; default: Console.Out.WriteLine ("I don't know what I see..."); break; } } return perceptions; } void agent_OnNewExternalActionSelectedHandler (ClarionAgentActionType externalAction) { Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture = new CultureInfo ("en-US"); if (scene != null) { robot.GetWheels ().stop (); switch (externalAction) { case ClarionAgentActionType.DO_NOTHING: if (nextSide == 0) { robot.GetWheels ().RotateRight (0.5); } else if (nextSide == 1) { robot.GetWheels ().RotateLeft (0.5); } else { robot.GetWheels ().Move (1); } if (currentSide != nextSide) ucounter = 0; if (ucounter > 30) { ucounter = 0; Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 8 ? 1 : 2) : 0; } currentSide = nextSide; ucounter++; break; case ClarionAgentActionType.ROTATE: { robot.GetWheels ().RotateRight (0.5); Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 7 ? 1 : 2) : 0; } break; case ClarionAgentActionType.MOVE: { robot.GetWheels ().Move (2); Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 7 ? 1 : 2) : 0; } break; case ClarionAgentActionType.LEFT: { robot.GetWheels ().Move (1); robot.GetWheels ().RotateLeft (1); Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 7 ? 1 : 2) : 0; } break; case ClarionAgentActionType.RIGHT: { robot.GetWheels ().Move (1); robot.GetWheels ().RotateRight (1); Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 7 ? 1 : 2) : 0; } break; case ClarionAgentActionType.BACK: { robot.GetWheels ().Move (-1); robot.GetWheels ().RotateLeft (1); Random rnd = new Random (); int r = rnd.Next (1, 10); nextSide = r > 4 ? (r < 7 ? 1 : 2) : 0; } break; default: break; } } } #endregion } } |
Code Snippet 5 - ClarionDEMO project Main.cs implementation.
3. CONCLUSIONS
Clarion is in general simple to understand and to implement but it can become complex depending on the complexity of the cognitive objectives. For developing this project, it was not required a profound knowledge of Clarion Framework but it required some extra effort to understand and develop the control dynamics of a real robot simulated in VRep environment.
Different from other simulation environmen where macro functions like move and distance to object are already implemented, VRep requires the implementation of all mechanisms involved in a moviment and that is the why the Pioneer P3-DX was choosen. The Pioneer P3-DS has enough complexibility for developing a solution but not too complex to control and implement a workable prototype.
The project phases can be listed as three as follows:
- Proxy. Solution implementation on both VRep Scene and Clarion application for bidirectional communication between the cognitive brain and the robot.
- Sensing. Solution implementation for understanding the varios sensor readings and provide sensing information for the cognitive brain.
- Actions. Solution implementation for defining actions based on the sensing information and sending commands to the robot via proxy.
Due to the complexity of the robot engine, as mentioned before, the more time consuming phase above was the Proxy implemention.
Theme by Danetsoft and Danang Probo Sayekti inspired by Maksimer

